
|
Click here for a
full-screen display that also shows fps.
|
You can use either the GrdWtr or GrdMap module together with the Ocean module to create a scrolling animated ocean surface that extends to the horizon. The GrdWtr module is a simplified version of the GrdMap module and creates a standard version of the ocean. The GrdMap module is a generalized module that gives the user the ability to define the geometries and textures for each grid. We will be expanding this module to work with land textures.
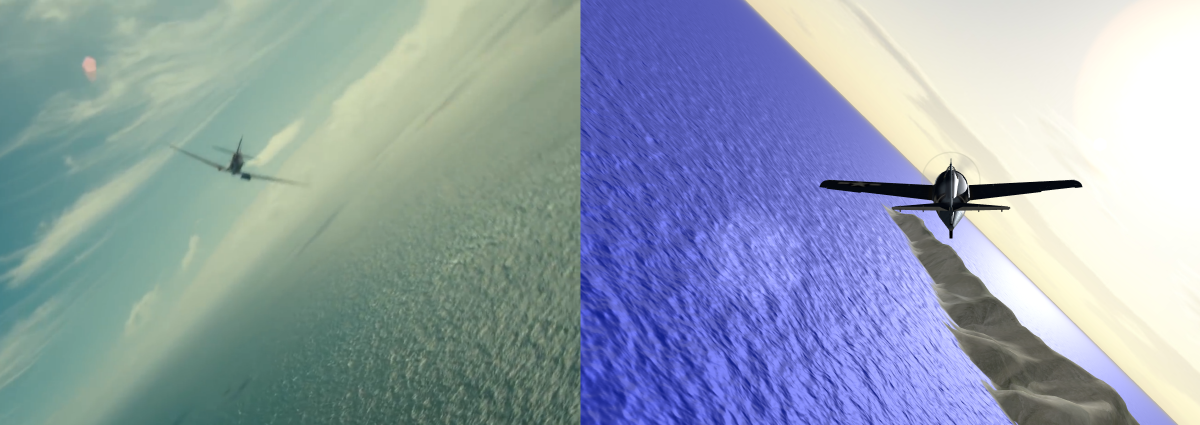
Both the GrdWtr and GrdMap modules use the same grid map. This grid map has 3 nested grids of squares. Grid0 has 16x16 squares, each of size GrdSiz (e.g. 1 mile, range = 8 miles). Grid1 has 16x16 squares, each of size GrdSiz*4 (e.g. 4 miles, range = 32 miles). Grid2 has 16x16 squares, each of size GrdSiz*16 (e.g. 16 miles, range = 128 miles).
The GrdWtr module is a simplified version of the GrdMap module and creates a standard version of the ocean. The ocean is untextured. The color of the ocean is a blend of the ocean color (WtrCol) variable and the SkyBox texture. Thus, merely changing the WtrCol variable may not have the desired effect since you also have to overcome the influence of the SkyBox texture. You can change the size of the smallest grid squares to increase resolution. However, this increases the risk of tiling as the altitude increases.
This references Version 2 of the Ocean program. For Version 1, see here.
You can insert these kinds of instructions at the beginning of your program to load the modules:
import {Ocean} from "three/addons/air/Ocean2.js"; // [v2: file name changed]
import {GrdMap} from "three/addons/air/GrdWtr.js";
You can add these variables to the beginning of your program:
/*= GRID DATA ================================================================*/
let GrdRes = 512;
let GrdSiz = 3200; // Size of Smallest Grid Square (meters)
let GrdSeg = 256; // Segments per Plane (256 = OK, 512 = too much)
/*= OCEAN MODULE =============================================================*/
let WndSpd = 20.0;
let WndHdg = 0.0;
let Choppy = 1;
let WavMax = 5; // Maximum wave height (set height of outer waves)
//
let Ocean1 = 0;
let wav1_ = {
// Sources
Res: GrdRes, // Resolution - segments per square (default = 512)
Siz: GrdSiz, // Size of Smallest Square = default = 3200m = 2 miles
WSp: WndSpd, // Wind Speed
WHd: WndHdg, // Wind Heading
Chp: Choppy, // default = 1
// Results
Dsp: 0, // Displacement Map Address
Nrm: 0, // Normal Map Address
};
let wavSp1 = 1.0; // Animation Speed Adjustment [v2: moved from wav_ and renamed]
let wavTm1 = 0; // Elapsed Time (as Adjusted) [v2: moved from wav_ and renamed]
/*= GRID MODULE ==============================================================*/
let grids = 0;
let grx_ = {
MSP: new THREE.Vector3 (), // MapSpdX, MapPosY, MapSpdZ (meters)
// Inputs
RCs: 16, // Squares in each of first 2 grids
Siz: GrdSiz, // Size of smallest square
Stp: 4, // Size multiplier for squares in last 2 grids
Seg: GrdSeg, // Segments for smallest square
WMx: WavMax, // Max wave height, used to lower outer squares
Col: WtrCol, // Color
Dsp: 0, // Displacement Map (from Ocean)
Nrm: 0, // Normal Map (from Ocean)
Env: 0, // EnvMap
// Results
Grd: [], // Index of Grids (0-2)
Geo: [], // Master Index of Basic Geometries
Mat: [], // Master Index of Basic Materials
};
You can add the following instructions to the Initialization section of your program:
// Initialize Ocean Ocean1 = new Ocean(renderer, wav1_); // [v2: no longer references camera or scene] // Set Aircraft Map Speed and Altitude grx_.MSP.z = beg_ZSpeed; // Z-Speed (N/S) in meters per second grx_.MSP.x = beg_XSpeed; // X-Speed (E/W) in meters per second grx_.MSP.y = beg_Altitude; // Altitude in meters // Load GrdMap Variables grx_.Dsp = wav_.Dsp; grx_.Nrm = wav_.Nrm; grx_.Env = envMap; // Initialize GridMap grids = new GrdMap(grx_, scene);
where renderer, camera and scene are the names of the variables for your renderer, camera and scene.
You can add the following instructions to the rendering section of your program:
// Update Grid Data grx_.MSP.z = new_ZSpeed; grx_.MSP.x = new_XSpeed; grx_.MSP.y = new_Altitude; // Render Ocean wavTm1 = difTim*wavSp1 || 0.0; [v2: variable moved from wav_ and renamed] Ocean1.render(wavTm1); [v2: only reference only time variable // Render Grids grids.update(grx_);
In order to compute wavTm1, your main program needs to include a timer. A simple example is shown below.
The GrdMap module is a more generalized module which allows you to define the Geometries and Materials for each set of Grids. For example, you can add a texture to the ocean and a static normal map to the farthest grids.
This references Version 2 of the Ocean program. For Version 1, see here.
You can add the instructions to the beginning of your program to load the modules:
import {Ocean} from "three/addons/air/Ocean2.js"; // [v2: file name changed]
import {GrdMap} from "three/addons/air/GrdWtr.js";
import * as BufferGeometryUtils from 'three/addons/utils/BufferGeometryUtils.js';
You can add these variables to your program:
/*= GRID DATA ================================================================*/
let GrdRes = 512;
let GrdSiz = 3200; // Size of Smallest Grid Square (meters)
let GrdSeg = 256; // Segments per Plane (256 = OK, 512 = too much)
let GeoAll = []; // Array used to assemble Grids
/*= OCEAN MODULE =============================================================*/
let WndSpd = 20.0;
let WndHdg = 0.0;
let Choppy = 1;
let WavMax = 5; // Maximum wave height (set height of outer waves)
//
let Ocean1 = 0;
let wav1_ = {
// Sources
Res: GrdRes, // Resolution - segments per square (default = 512)
Siz: GrdSiz, // Size of Smallest Square = default = 3200m = 2 miles
WSp: WndSpd, // Wind Speed
WHd: WndHdg, // Wind Heading
Chp: Choppy, // default = 1
// Results
Dsp: 0, // Displacement Map Address
Nrm: 0, // Normal Map Address
};
let wavSp1 = 1.0; // Animation Speed Adjustment [v2: moved from wav_ and renamed]
let wavTm1 = 0; // Elapsed Time (as Adjusted) [v2: moved from wav_ and renamed]
/*= GRID TEXTURES ============================================================*/
// Textures (these need to be loaded in Main Program)
// Diffuse Map (Optional - All Grids)
let WtrSrc = "https://threejs.org/examples/textures/waternormals.jpg"; // 0 = Don't load
let WtrTxt = 0;
// Normal Map (Grid2 Only)
let NrmSrc = "https://threejs.org/examples/textures/waternormals.jpg";
let WtrNrm = 0;
/*= GRID MODULE ==============================================================*/
let grids = 0;
let grx_ = {
MSP: new THREE.Vector3 (), // MSX, MPY, MSZ (meters)
RCs: 16, // Squares in each of first 2 grids
Siz: GrdSiz, // Size of smallest square
Stp: 4, // Size multiplier for squares in last 2 grids
Seg: GrdSeg, // Segments for smallest square
Grd: [], // Index of Grids (0-2)
Geo: [], // Master Index of Basic Geometries
Mat: [], // Master Index of Basic Materials
WMx: WavMax, // Max wave height, used to lower outer squares
};
The GrdMap module allows you to create custom textures and geometries which are then loaded into the GridMap. You can add the GeoMap Functions below to your main program, which will allow you to add custom textures to the ocean and to customize your materials:
/*= GEOMAT ===================================================================*/
function loadGeoMat() {
// Load Diffuse Map (Optional - All Grids)
if (WtrSrc) { // Load the texture only if there is an address
txtrLoader.load(WtrSrc, function(texture) {
texture.format = THREE.RGBAFormat;
texture.magFilter = THREE.LinearFilter;
texture.minFilter = THREE.LinearMipMapLinearFilter;
texture.generateMipmaps = true;
texture.wrapS = texture.wrapT = THREE.RepeatWrapping;
texture.offset.set(0,0);
texture.needsUpdate = true;
WtrTxt = texture;
});
}
// Normal Map (Grid2 Only)
txtrLoader.load(NrmSrc, function(texture) {
texture.format = THREE.RGBAFormat;
texture.magFilter = THREE.LinearFilter;
texture.minFilter = THREE.LinearMipMapLinearFilter;
texture.generateMipmaps = true;
texture.wrapS = texture.wrapT = THREE.RepeatWrapping;
texture.offset.set(0,0);
texture.repeat.set(16,16);
texture.needsUpdate = true
WtrNrm = texture;
});
}
function initGeoMat() {
// Define the Materials and Geometries Referenced in grx_.Geo and grx_.Mat
let siz = grx_.Siz;
let stp = grx_.Stp;
/*- Grid0 ----------------------------------------------------------------*/
let n = 0;
let seg = grx_.Seg;
grx_.Mat[n] = new THREE.MeshPhysicalMaterial({
color: WtrCol,
map: WtrTxt, // 0 if no map loaded
displacementMap: wav_.Dsp, // Animated displacementMap
normalMap: wav_.Nrm, // Animated normalMap
envMap: envMap,
normalScale: new THREE.Vector2(2.5,2.5),
metalness: 1.0, // 1 for max reflection
roughness: 0.7, // 0 for max reflection
reflectivity: 0.5, // 1 for max reflection
envMapIntensity: 5, // max reflection suggested = 5
premultipliedAlpha: true,
});
grx_.Geo[n] = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(siz,siz,seg,seg);
grx_.Geo[0].rotateX(-Math.PI * 0.5);
/*- Grid1 ----------------------------------------------------------------*/
// This far out, you cannot see the Animated displacementMap,
// but you can still see the Animated normalMap
n = 1;
grx_.Mat[n] = new THREE.MeshPhysicalMaterial({
color: WtrCol,
map: WtrTxt, // 0 if no map loaded
normalMap: wav_.Nrm, // Animated normalMap
envMap: envMap,
normalScale: new THREE.Vector2(2.5,2.5),
metalness: 1.0, // 1 for max reflection
roughness: 0.7, // 0 for max reflection
reflectivity: 0.5, // 1 for max reflection
envMapIntensity: 5, // max reflection suggested = 5
premultipliedAlpha: true,
});
// This allows you to repeat the Animated normalMap in this 4x4 Square
let idx = 0;
let ctr = (0.5*stp-0.5)*siz; // 2 = 0.5; 3 = 1.0; 4 = 1.5
for (let z = 0; z < stp; z++) {
for (let x = 0; x < stp; x++) {
GeoAll[idx] = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(siz,siz);
GeoAll[idx].rotateX(-Math.PI * 0.5);
GeoAll[idx].translate(x*siz-ctr, 0, z*siz-ctr);
idx++;
}
}
let max = stp*stp;
for (let i = 1; i < max; i++) {
GeoAll[0] = BufferGeometryUtils.mergeGeometries([GeoAll[0], GeoAll[i]], false);
}
grx_.Geo[n] = GeoAll[0];
/*- Grid2 ----------------------------------------------------------------*/
// This far out, you cannot see the animation, so you can use a static normalMap
n = 2;
siz = grx_.Siz*grx_.Stp*grx_.Stp;
grx_.Mat[n] = new THREE.MeshPhysicalMaterial({
color: WtrCol,
map: WtrTxt, // 0 if no map loaded
normalMap: WtrNrm, // Static normalMap
envMap: envMap,
normalScale: new THREE.Vector2(2.5,2.5),
metalness: 1.0, // 1 for max reflection
roughness: 0.7, // 0 for max reflection
reflectivity: 0.5, // 1 for max reflection
envMapIntensity: 5, // max reflection suggested = 5
premultipliedAlpha: true,
});
grx_.Geo[n] = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(siz,siz);
grx_.Geo[2].rotateX(-Math.PI * 0.5);
}
You can add the following instruction to the loading section of your program:
loadGeoMat();
You can add the following instructions to the Initialization section of your program:
// Initialize Ocean Ocean1 = new Ocean(renderer, wav1_); // Define GridMap Materials and Geometries initGeoMat(); // Initialize Grid Materials // Set Aircraft Map Speed and Altitude grx_.MSP.z = beg_ZSpeed; // Z-Speed (N/S) in meters per second grx_.MSP.x = beg_XSpeed; // X-Speed (E/W) in meters per second grx_.MSP.y = beg_Altitude; // Altitude in meters // Initialize GridMap grids = new GrdMap(grx_, scene);
where renderer, camera and scene are the names of the variables for your renderer, camera and scene.
You can add the following instructions to the rendering section of your program:
// Update Grid Data grx_.MSP.z = new_ZSpeed; grx_.MSP.x = new_XSpeed; grx_.MSP.y = new_Altitude; // Render Ocean wavTm1 = difTim * wav_.Spd || 0.0; Ocean1.render(wavTm1); // Render Grids grids.update(grx_);
In order to compute wav._DTm, your main program needs to include a timer. A simple example is shown below.
Here is a simple timer you can use to update wav_.DTm.
Initialize the clock in the variables section with this command and general variables:
let clock = new THREE.Clock(); let oldTim, nowTim, difTim = 0;
In your render loop, insert the following:
nowTim = clock.getElapsedTime(); difTim = nowTim-oldTim; oldTim = nowTim; wavTm1 = difTim * wav_.Spd || 0.0;
As altitude increases, you might notice a "tiling" problem. You can address this problem by increasing the size of the smallest grid. However, this will result in a decrease in resolution at lower altitudes.
| the Ocean class module. | ||
| a GrdMap module in which water textures are imported. | ||
| a GrdMap module that automatically creates water textures. | ||
| a program that uses the Ocean and GrdMap (GrdMap.js) modules. | ||
| a version of the above that you can run locally. | ||
| a program that uses the Ocean and GrdMap (GrdWtr.js) modules. | ||
| a version of the above that you can run locally. |